Infervision is a Chinese artificial intelligence high-tech company specialized in medical AI and committed to applying deep learning techn...
This is time-consuming, laborious, and, frankly, quite tedious. Simple human error, often caused by fatigue, means mistakes being made and important diagnoses being missed. This problem inspired Chen Kuan, founder of medical image diagnostics startup Infervision, to focus his work with deep learning and image recognition on the world of medicine.
 |
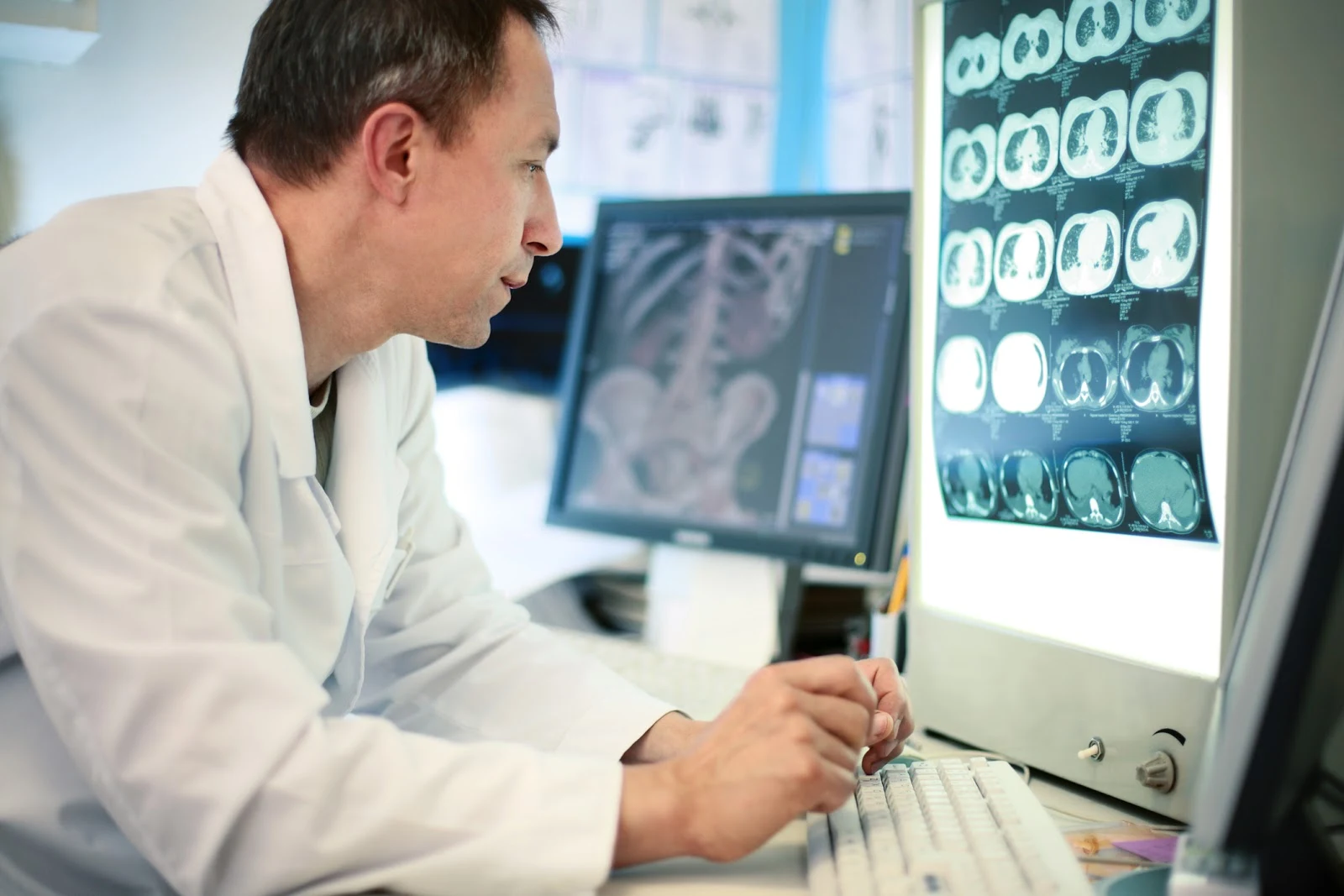
| A computerized tomography (CT) or computerized axial tomography (CAT) scan combines data from several X-rays to produce a detailed image of structures inside the body. |
Kuan and two team members spent a whole year working on a pilot project at the Szechwan People’s Hospital, learning how the Infervision tool they were building could be integrated with existing hospital systems. During that year, they began training and teaching their algorithms.
This entailed using real-life data from previous scan images to increase the model’s accuracy at identifying signs of cancerous growth in lung scans. In 2015, after the successful pilot, Infervision gained investment, and the project expanded to cover a number of other Chinese hospitals. Today, the business is looking for international partners to further help lighten the load for radiologists around the world.
Kuan is keen to emphasise that Infervision’s mission is not to eliminate the need for human radiologists. Rather, its technology is designed to help radiologists, by enabling them to diagnose cancer more accurately and efficiently than ever before.“In China there are just 80,000 radiologists who have to work through 1.4 billion radiology scans every year. By using AI and deep learning, we can augment the work of those doctors. In no way will this technology ever replace doctors – it is intended to eliminate much of the highly repetitive work and empower them to work much faster,” says Kuan.
The technical details
Deep learning uses deep neural networks that mimic how human brain functions. Data is passed along networks of nodes, and these networks adapt according to whatever data they are processing as moves from node to node. This way, the neural networks can more efficiently process the next bit of data that comes along, based on the data that came before it. This ability to “learn” from data and the ability of a system to effectively teach itself is what makes deep learning so powerful.
Kuan and his team used a method that’s called “supervised learning”, which means using datasets where the outcome is known (in this case, a diagnosis of cancer) to “teach” the model how to react in the future. As Kuan puts it, “Basically what I did was teach it to predict if an x-ray is normal or not.”
Ideas and insights you can steal
It’s exciting to see AI being used in this way. And, of course, this is precisely the sort of task that machines are brilliant at; a machine can keep working and working without ever getting bored or suffering a momentary loss of concentration.
What’s particularly interesting is Kuan’s vision of AI technology augmenting the work of human radiologists, rather than replacing them. With so many stories about increasing automation and the threat to human jobs, it’s a timely reminder of how AI can help us humans work much smarter.